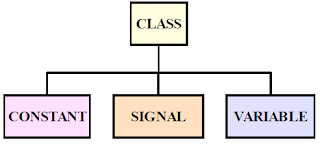
• Class indicates how the object is used in the module and what can be done with that object.
• Type indicates what type of data the object contains.
• Each object belongs to one of the following class:
– CONSTANT
– SIGNAL
– VARIABLE
Constants
• These are identifiers with fixed values.
• The value is assigned only once when declared.
• Values cannot be changed during simulation
CONSTANT bus_width : INTEGER :=16 ;
CONSTANT CLK_PERIOD : TIME :=15 ns ;
• Constants make the design description more readable.
• Design changed at later time becomes easy.
Signals
Equivalent to wires within a circuit
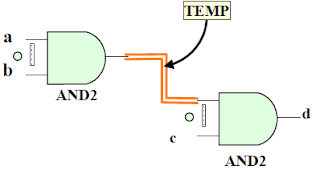
Example:
architecture and_gate of myand is
signal TEMP : STD_LOGIC ;
begin
U1 : AND2 portmap ( a, b, TEMP ) ;
U2 : AND2 portmap (TEMP, c , d ) ;
end and_gate ;
• Thus signals are used :
– to connect design entities together and communicate changes in values within a design
– instead of INOUT mode
• Each signal has a history of values i.e. they hold a list of values which include current value of the signal and a set of possible future values that can appear on the signal.
• Computed value is assigned to signal after specified delay called DELTA DELAY.
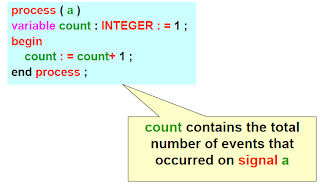
Variables
• These are objects with single current value.
• They are used to store the intermediate values between the sequential statements.
• Variable assignment occurs immediately.
• Variables can be declared and used inside the process statement only. But they retain their value throughout the entire simulation.
Example :
information shared by www.irvs.info
No comments:
Post a Comment